Microgrid Market Overview: Powering a Resilient and Sustainable Energy Future
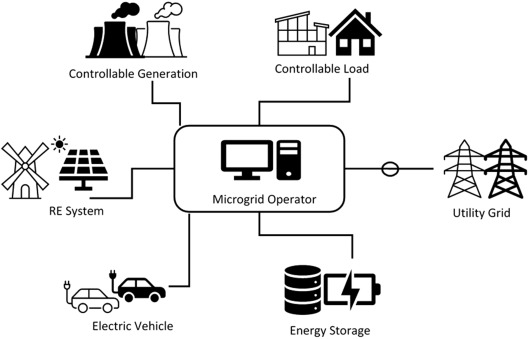
What is a Microgrid?
A microgrid is a compact, localized energy system that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main electrical grid. It provides power to specific areas such as hospitals, university campuses, military bases, and commercial buildings. Unlike traditional power systems that rely entirely on centralized grids, microgrids are designed to deliver electricity even when disconnected from the main supply.
This flexibility allows microgrids to act as electrical islands, particularly during emergencies or blackouts, ensuring continued energy access for critical infrastructure. Moreover, smart microgrids incorporate advanced technology to manage energy production and distribution, often including renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
As the world shifts toward decentralized and sustainable energy systems, microgrids are becoming an essential component of the modern power infrastructure.
Market Snapshot and Growth Outlook
The global microgrid market has shown robust growth in recent years, driven by increased demand for clean, resilient, and efficient power systems. According to market research, the market was valued at USD 38.3 billion in 2023. It is projected to grow to USD 44.12 billion in 2024, with a forecasted value of USD 136.86 billion by 2032. This reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.2% during the 2025–2032 period.
This growth is fueled by several factors including rising concerns about energy security, climate change, and the reliability of centralized grids. Organizations, governments, and communities are investing in microgrids to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and ensure uninterrupted energy supply.
Key Drivers of the Microgrid Market
1. Energy Resilience and Reliability
One of the primary drivers behind microgrid adoption is the need for energy resilience. Microgrids provide a reliable power source during outages, which is especially critical for sectors like healthcare, defense, and manufacturing. By isolating from the central grid when necessary, microgrids ensure that essential services continue operating without interruption.
2. Integration of Renewable Energy
Microgrids support the integration of renewable energy technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines, and biomass systems. This not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also minimizes environmental impact. As global efforts to decarbonize the energy sector intensify, microgrids are becoming a popular solution for delivering clean, sustainable power.
3. Government Support and Investment
Governments around the world are implementing favorable policies, subsidies, and funding programs to promote microgrid development. Initiatives aimed at modernizing the energy infrastructure and reducing greenhouse gas emissions are accelerating the adoption of microgrid solutions across various regions.
Market Segmentation
Understanding the market’s segmentation offers insights into how microgrids are being utilized across different industries and regions.
By Power Source:
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP): Efficiently utilizes both electricity and heat.
- Solar Photovoltaics (PV): Converts sunlight into electricity.
- Fuel Cells: Offers clean and efficient energy with minimal emissions.
- Diesel Generators: Traditional power backup for areas without renewable access.
By Application:
- Commercial Buildings: Provides consistent energy for business continuity.
- Government & Institutions: Ensures operational reliability during crises.
- Utilities: Supplements centralized power supply and reduces load.
- Defense: Maintains energy security in critical defense installations.
- Educational Campuses: Promotes sustainability and reduces costs.
By Region:
- North America: Leading in adoption due to advanced infrastructure and government support.
- Asia-Pacific: Witnessing rapid growth due to urbanization and electrification of rural areas.
- Europe: Strong focus on renewable energy and smart grid technologies.
- Latin America: Gradual adoption driven by power reliability needs.
- Middle East & Africa: Increasing use in remote and off-grid locations.
Opportunities and Challenges
Key Challenges
Despite their benefits, microgrids face certain hurdles:
- High Maintenance Costs: Regular upkeep and technical oversight are required, which can be expensive.
- Regulatory Barriers: Differing grid standards, policies, and approval processes across regions complicate deployment.
Emerging Opportunities
There are also significant opportunities that are transforming the landscape:
- Smart Grid Integration: Technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Internet of Things (IoT) are being embedded into microgrids for intelligent energy management and predictive maintenance.
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging: As the demand for EVs grows, microgrids are emerging as decentralized power sources for charging infrastructure, particularly in areas with limited grid access.
Key Industry Players
The microgrid market is competitive, with several major companies playing a significant role in advancing technology and deployment. Some of the top players include:
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric
- ABB Ltd.
- General Electric (GE)
- Honeywell International
These organizations are leading the development of energy storage systems, grid control software, and hybrid power solutions, further expanding the reach and reliability of microgrid applications.
Emerging Trends in the Microgrid Market
Growing Use of Renewable Energy and Storage Solutions
One of the most significant trends shaping the microgrid industry is the increasing use of clean energy and storage technologies. More communities and companies are turning to microgrids equipped with solar, wind, and battery storage systems to reduce their carbon footprint and enhance energy reliability.
These systems store excess electricity during periods of low demand and discharge it during peak usage, improving overall energy efficiency.
Environmental Concerns Driving Adoption
Environmental awareness is influencing energy decisions at all levels—from individuals to corporations and governments. Concerns about pollution and climate change are prompting a move away from traditional, carbon-intensive energy sources. Microgrids, especially those incorporating renewable power and advanced storage, offer a cleaner alternative.
Recent Developments
The microgrid industry continues to evolve rapidly with significant technological advancements:
- July 2024: Siemens introduced an advanced microgrid management system powered by AI and IoT. This solution offers real-time control and enhances system performance and reliability.
- June 2024: ABB launched a scalable microgrid platform integrating smart grid functions with renewable power and battery storage. It aims to improve energy access in remote and underserved areas.
- August 2024: GE announced a digital microgrid solution focused on predictive analytics and cost reduction. This development supports urban and rural energy sustainability goals.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, microgrids are poised to become a cornerstone of the global energy landscape. With the rise of smart cities, electric vehicles, and distributed energy systems, microgrids provide a flexible and future-ready solution. Their ability to operate independently, integrate clean energy, and support critical infrastructure makes them essential in achieving energy security, cost efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
As innovation continues and supportive policies expand, the microgrid market is expected to accelerate, shaping a resilient and decentralized future for energy.
📘 For a complete analysis, read the full SkyQuest report: https://www.skyquestt.com/report/microgrid-market



